Industrial Noise - Common Challenges in Noisy Factories
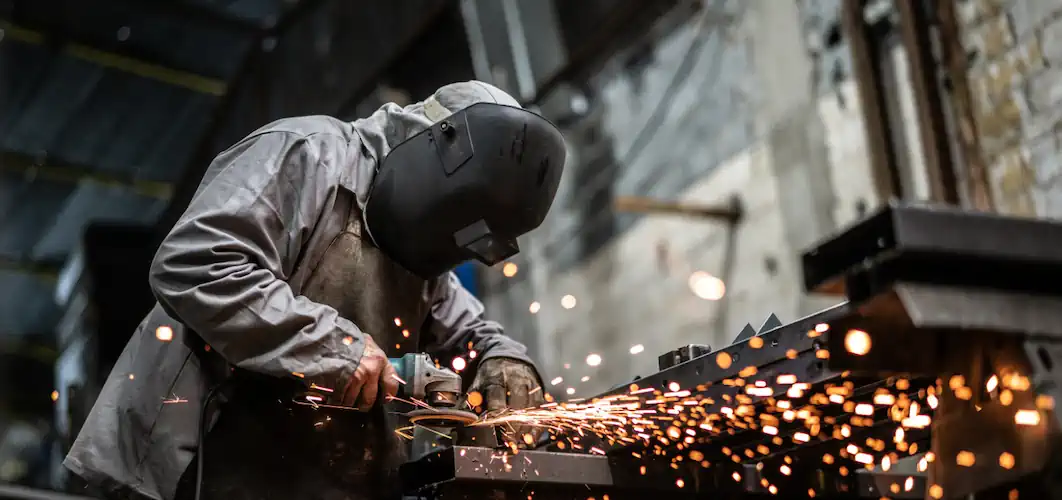
Industrial noise is a pervasive challenge in many factory environments, posing significant risks to both workers and surrounding communities. The sources of industrial noise range from the machinery and equipment used in industrial processes to the noise emissions generated by various production activities.
This article explores the complexities of industrial noise, its impact on human health, and the various noise control measures that can help mitigate its adverse effects, especially the use of ear protection.

Table of Contents
-
Industrial Noise Pollution and Its Sources
-
Industrial Noise Levels in Modern Factories
-
The Negative Effects of Noise Pollution on Workers
-
Noise Reduction Strategies for Noisy Factories
-
Protecting Workers with Personal Protective Equipment
-
Long-term Solutions for Managing Industrial Noise Pollution
-
Addressing Industrial Noise for a Safer Workplace
Industrial Noise Pollution and Its Sources
Industrial noise pollution refers to the unwanted or excessive sound that disrupts the working environment. The industrial processes involved in manufacturing, construction, and other industrial activities often result in high noise levels. Prolonged exposure to industrial noise pollution can adversely affect workers' hearing, causing permanent hearing damage. Excessive noise also leads to other negative effects such as sleep disturbances, communication issues, and cardiovascular diseases.
The noise emitted from industrial equipment and machinery can be classified as hazardous noise when it exceeds the permissible noise levels determined by the World Health Organization (WHO) and local regulatory bodies. Prolonged exposure to hazardous noise can result in noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL), putting workers at risk without adequate noise control measures.

Industrial Noise Levels in Modern Factories
Industrial noise is an unavoidable byproduct of many activities, particularly in large manufacturing and processing facilities. Noise levels in these settings can be extremely high, often exceeding the permissible limits set by regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Industrial sounds originate from sources like machinery, ventilation systems, conveyor belts, and heavy equipment vibrations.
Machinery Noise
A significant aspect of industrial noise is the high-intensity sounds produced by heavy machinery. Machines such as presses, mills, and generators contribute greatly to pollution within factories. Prolonged exposure to this constant noise can lead to hearing loss and other health issues, particularly for employees in environments with hazardous noise levels for extended periods.
The Negative Effects of Noise Pollution on Workers
Noise pollution in industrial settings has effects beyond hearing loss. Extended exposure to loud, high-frequency sounds can lead to stress, fatigue, and mental health issues. Prolonged noise exposure is also linked to cardiovascular diseases, as the stress caused by excessive sound can elevate blood pressure and strain the heart. These effects can significantly reduce workers' quality of life and productivity.
Adverse Effects on Human Health
Industrial noise has significant adverse effects on workers, including a decline in their overall quality of life. Constant exposure to loud noises in the workplace can lead to hearing loss and communication difficulties, making it challenging for employees to hear important instructions, which may affect the overall performance quality. Noise pollution from industrial activities also negatively impacts nearby communities and contributes to other forms of pollution, such as water pollution, harming local ecosystems.

Noise Reduction Strategies for Noisy Factories
Engineering Controls: Sound Barriers and Equipment Modifications
One of the most effective ways to reduce industrial noise is through engineering controls. Noise barriers can be installed around noisy machinery or equipment to reduce the transmission path of sound waves. Modifying or upgrading equipment to be quieter can significantly lower the excessive sound produced. Regular maintenance of machinery helps prevent excessive noise due to wear and tear, ensuring that the noise produced remains within acceptable noise levels. These measures protect workers and help mitigate noise pollution's impact on nearby residents and the environment.
Administrative Controls: Limiting Exposure Time and Rotation
Administrative controls are another important aspect of noise reduction. Limiting workers' exposure to noisy areas by rotating shifts or implementing strict exposure time limits can help minimize the negative effects of occupational noise exposure. Additionally, soundproofing the work environment and separating noisy processes from quieter areas can reduce the impact of unwanted sound on workers. By managing noise exposure in various aspects of the workplace, companies can help prevent long-term health issues related to excessive noise.
Protecting Workers with Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment plays a vital role in reducing workers' exposure to hazardous noise. In noisy industrial environments, workers should wear PPE designed to block high-intensity sound. Protective gear is crucial for preventing hearing damage and minimizing noise-induced hearing loss. Without personal protective equipment (PPE), noise can significantly harm health and safety.
In addition to other forms of personal protective equipment, hearing protection is essential for workers exposed to hazardous noise levels in industrial settings. Hearing PPE includes earplugs, earmuffs, and custom-molded ear protection designed to reduce noise exposure and prevent permanent hearing damage. Proper use of hearing protection is a key component of noise control and occupational health.
Without adequate hearing PPE, workers face immediate risks such as temporary hearing impairment and long-term consequences, including permanent hearing loss. By using hearing protection, workers not only safeguard their own health but also contribute to reducing noise pollution in the surrounding community.

Long-term Solutions for Managing Industrial Noise Pollution
Addressing industrial noise pollution requires a commitment to creating safer workplaces for employees. Beyond immediate noise control measures, businesses should invest in strategies and technologies to manage noise levels sustainably. These benefit workers, neighboring communities, and the environment by reducing the detrimental effects of noise pollution and its broader environmental impacts.
Noise Control Technology and Future Trends
Advancements in noise control technology, like quieter machinery and better soundproofing materials, are reducing the impact of industrial noise. Integrating noise management systems into new facility designs ensures that noise pollution is minimized. For factories facing ongoing challenges, regular evaluations and updated control measures are essential for protecting workers and communities while minimizing environmental impact. Effective long-term solutions reduce industrial noise and enhance workplace safety and community well-being.
Addressing Industrial Noise for a Safer Workplace
Industrial noise is a serious concern that can lead to health issues like hearing loss, cardiovascular diseases, and sleep disturbances. In noisy settings, workers face harmful sounds that can affect their health in the long run.
Noise reduction strategies, such as engineering controls, administrative measures, and high quality PPE, are essential in minimizing these risks. Properly designed machinery, noise barriers, and regular maintenance can significantly lower noise emissions.
By prioritizing noise control and ensuring compliance with standards and safety regulations, industrial facilities can protect workers from harmful noise exposure.