Essential PPE for Metal Fabrication: A Brief Guide
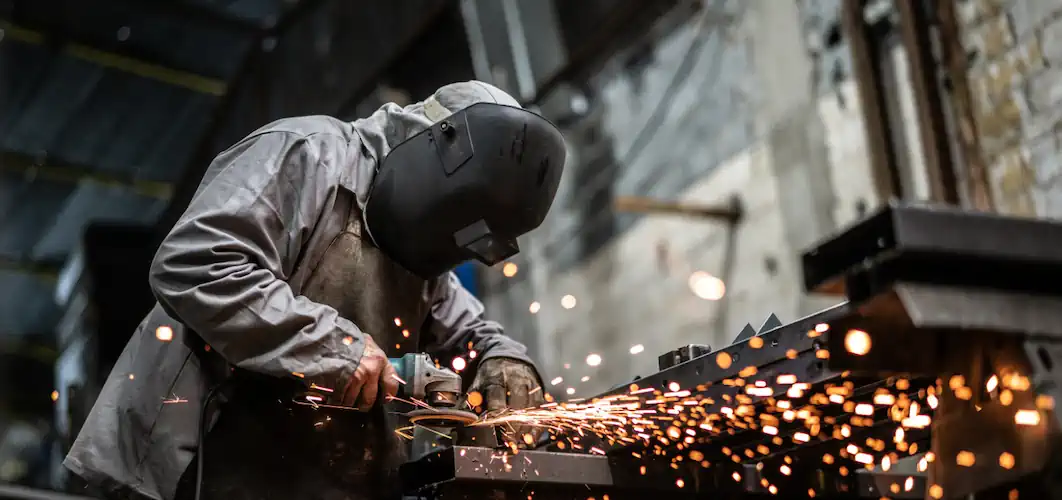
Metal fabrication is a process that requires the appropriate PPE to ensure safety and prevent potential hazards. By cutting and welding metal structures, shaping and finishing metal components, metal fabrication has a wide range of applications that come with inherent risks.
What PPE is needed for Metal Fabrication?
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) refers to proactive equipment and garments designed to protect the wearer and minimize their exposure to hazards. This is why workers in the metal fabrication field should wear the following PPE:
1. Eye Protection
In metal fabrication shops, tasks like cutting, grinding, and welding produce particles, intense light, and sparks that pose eye injury risks. Safety glasses, goggles, and face shields are crucial as they prevent debris from entering the eyes and shield against harmful UV rays emitted during welding.

- Face Shields: Crucial for high-intensity tasks like welding and foundry work. They cover the entire face, providing a wide shield against intense light, sparks, and potential splatter.
- Safety Glasses: Basic eye protection commonly used in metalworking. They shield against small debris and offer general eye protection.
- Goggles: These provide a more comprehensive coverage area around the eyes, protecting against splashes, welding fumes, and larger debris compared to safety glasses.
2. Respiratory Protection
Fumes, dust, and gases are often produced in metal fabrication, and pose as respiratory risks. Adequate ventilation systems, including fume extractors and local exhaust systems, play a pivotal role in maintaining clean air and minimizing the inhalation of hazardous materials.
- Particulate Respirators (N95 Masks): Effective against airborne particles, these filters don’t provide protection against gases or vapors. They filter out solid particulates, making them ideal for tasks that produce dust.
- Respirators with Cartridges: Respirators with cartridges are tailored to filter gases and vapors found in metal fabrication.
3. Ear Protection
The machinery and tools used in metal fabrication emit high levels of noise that can cause long-term hearing damage. Ear protection, such as earplugs and earmuffs, significantly reduces noise exposure. Properly fitted earplugs or earmuffs are essential to safeguard workers from potentially irreversible hearing impairment.

4. Head Protection
Head injuries can occur due to falling objects or collisions in confined workspaces. Hard hats are indispensable in these environments as their design includes a shock-absorbing suspension system, shielding workers from impact and penetration hazards. On the other hand, bump caps are designed to shield again minor bumps, scrapes and cuts, making it suitable for low overhead hazards.

5. Protective Clothing
Full-body protection is essential in metalworking to safeguard against burns, cuts, and sparks. Flame-resistant clothing, coveralls, or work jackets are critical components of PPE. They act as a barrier against welding sparks, intense heat, and sharp metal edges, ensuring comprehensive protection for workers.
- Flame-Resistant Clothing: Essential in metalworking and foundries due to exposure to high heat and sparks. These garments are designed to resist ignition, reducing the risk of burns.
- Welding Jackets and Aprons: Constructed from heavy-duty materials to protect against sparks, splatter, and heat generated during welding operations.
Specialized PPE in metalworking and foundry industries is designed to address most hazards. Tailored materials, design features, and protective capabilities ensure maximum safety for workers.
What are the Standards for PPE in Fabrication?
Various organizations set standards to ensure the quality of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in metal fabrication. Prominent standards include:
Eye and Face Protection
ANSI/ISEA Z87.1: The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard for eye and face protection outlines criteria for impact resistance, coverage, optical quality, and more for safety glasses, goggles, and face shields.
Respiratory Protection
OSHA 1910.134:The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has regulations for respiratory protection, outlining requirements for respirator use, fit testing, training, and medical evaluations.
EN 149: European standard for filtering half masks used as respiratory protective devices.
Ear Protection
ANSI/ASA S3.19-1974: The American National Standards Institute and the Acoustical Society of America (ASA) standards for hearing protection devices set criteria for the attenuation (noise reduction) levels that earplugs and earmuffs should achieve.
Head Protection
ANSI/ISEA Z89.1: This standardizes performance criteria for industrial head protection, specifying requirements for impact and penetration resistance of hard hats used in various industries, including metalworking.
Protective Clothing
NFPA 70E: This standard by the National Fire Protection Association provides guidelines for flame-resistant clothing and protective gear to safeguard against arc flash hazards in electrical work, including metal fabrication involving electrical equipment.
What to Consider when Selecting the PPE for Fabrication?
When choosing PPE for metal fabrication, consider key criteria for maximum effectiveness and worker safety:
-
Hazard Assessment
Understand the specific risks and hazards present in the metal fabrication environment, including exposure to heat, sparks, sharp edges, fumes, chemicals, noise, falling objects, and electrical hazards.
-
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that the chosen PPE complies with relevant safety standards and regulations established by organizations like ANSI, OSHA, ASTM, or other regional safety authorities.
-
Ergonomics and Mobility
PPE should not hinder workers' mobility or dexterity, allowing them to perform their tasks effectively without compromising safety.
-
Feedback and Evaluation
Regularly assess the effectiveness of the chosen PPE through worker feedback, incident reports, and evaluations to make necessary adjustments and improvements.