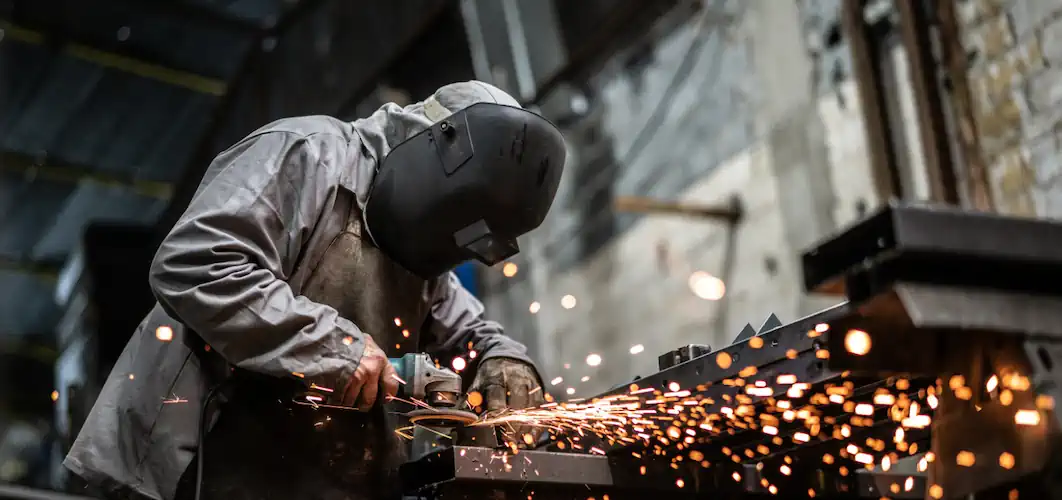
Proximity Suits: Ensuring Worker Safety in Extreme Environments
In the world of metallurgy and foundry industries, the pursuit of progress goes hand in hand with working in extreme conditions. But in the midst of this excitement, there's a concern that should never be overlooked – the safety of the workers who make these industries thrive. This is where proximity suits step in, as the heroes safeguarding the brave men and women who dare to work in the midst of extreme environments.
Click Here to Buy!
What are Proximity Suits?
Proximity suits are specialized protective garments designed to safeguard workers from the extreme conditions prevalent in industries such as metallurgy and foundry. These suits are not your typical workwear; they are meticulously engineered with advanced materials and construction to provide an exceptional level of protection against intense heat, flames, molten metal splashes, and other potential hazards.
An entry suit is different from a proximity suit in material and purpose. Entry suits have a higher fire resistance compared to proximity gear because the former is used for protection against total flame engulfment. Aluminized suits are not useful when heat from the fire is directly conducted through the material, which is why entry suits are built with vermiculite or similar materials that conduct less heat.
For industrial workers in the foundry and metallurgy sectors, the key features of proximity suits should include:
1. Multi-Layer Construction
Proximity suits are crafted with multiple layers, each serving a specific purpose. The outermost layer is made from heat-resistant materials that repel flames and molten splashes. Beneath this layer, insulating materials are used to minimize heat transfer to the wearer, creating a barrier against extreme temperatures.
2. Heat Resistance
The primary function of proximity suits is to shield workers from high temperatures. The materials used in these suits are chosen for their exceptional heat resistance properties, allowing workers to operate safely in environments where traditional clothing would be inadequate.
3. Ventilation Systems
Working in extreme heat can be uncomfortable and even dangerous. Proximity suits often feature built-in ventilation systems that facilitate air circulation within the suit. This helps to dissipate excess heat and maintain a comfortable temperature for the wearer.
4. Flexibility and Mobility
Unlike bulky protective gear that restricts movement, proximity suits are designed to provide both protection and flexibility. These suits are tailored to allow workers to move freely and perform their tasks without hindrance.
5. Reinforced Seams and Closures
To prevent molten splashes and flames from infiltrating the suit, proximity suits are equipped with reinforced seams and closures. This ensures that vulnerable areas remain tightly sealed, maintaining the integrity of the protective layers.
6. Customized Designs
Different industries and work scenarios have varying safety requirements. Proximity suits come in a range of designs, each catering to specific needs. A suit with an aluminized hood and built-in gloves provides complete proximity protection. Some have additional layers for enhanced insulation to cater to different workplace demands.
7. Reflective Elements
Visibility is crucial in any work environment, and proximity suits often incorporate reflective strips or elements. These enhance the visibility of workers in low-light conditions, further ensuring their safety.
Thermal Protective Performance (TPP) and its Significance
Thermal Protective Performance (TPP) is a critical measure used to evaluate the heat protection provided by protective clothing, including proximity suits. It quantifies the ability of a fabric or ensemble to insulate against heat and prevent burns in the event of exposure to high temperatures. TPP takes into account multiple factors, including the fabric's heat resistance, its insulating properties, and its ability to protect the wearer from radiant heat, convective heat, and contact heat.
The TPP rating is expressed in terms of the time it takes for the fabric to transmit enough heat to raise the wearer's skin temperature by a specific threshold. A higher TPP rating indicates better heat protection and a longer time the wearer can remain in a high-temperature environment before experiencing skin damage.

The Anatomy of Proximity Suits
The primary materials used in proximity suits are carefully chosen to provide exceptional heat resistance, flame protection, and overall durability. These materials work together to create a barrier between the wearer and the hazardous environment. While variations exist based on manufacturers and designs, here are some common primary materials used in proximity suits:
1. Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers are among the most commonly used materials for the outer layer of proximity suits. These fibers are known for their exceptional heat resistance, flame retardancy, and strength. They effectively shield workers from direct contact with flames and molten metal splashes.
2. Fiberglass and Silica
For insulating layers, materials like fiberglass and silica are frequently employed. These materials have excellent thermal insulation properties, helping to minimize heat transfer from the outer layer to the wearer's body. They create a thermal barrier that keeps extreme temperatures at bay.
3. Aluminized Fabrics
Aluminized fabrics are often used in proximity suits, especially in high-temperature environments. These fabrics have a reflective aluminum coating that enhances the suit's heat resistance and provides additional protection against radiant heat.
Vacuum-deposited aluminized materials play a crucial role in enhancing the heat protection and radiant heat reflection capabilities of proximity suits. These materials are a specialized type of coating applied to the surface of fabrics to provide improved heat resistance, especially in high-temperature environments.
Understanding the intricate construction of proximity suits is like peeling back the layers of a safety fortress. These specialized garments are not just clothing; they're a meticulously engineered shield against the formidable challenges posed by extreme environments in metallurgy and foundry industries.
1. Outer Layer
The first line of defense is the outer layer. Crafted from advanced heat-resistant materials, this layer acts as a fortress against flames and molten metal splashes. It's the guardian that repels the scorching elements, preventing them from reaching the wearer's skin.
2. Insulating Layers
Beneath the rugged exterior, lies a series of insulating layers. These layers are like a thermal cocoon, designed to minimize heat transfer from the external environment to the wearer's body. Just as a thermos keeps your coffee warm, these insulating layers keep extreme temperatures at bay.
3. Ventilation System
Imagine being wrapped in protective layers, yet feeling refreshingly cool. Proximity suits often feature a clever ventilation system that creates a flow of air within the suit. This not only prevents the accumulation of heat but also ensures that the wearer remains comfortable even in the most heated situations.
4. Moisture Barrier
Some proximity suits incorporate a moisture barrier layer to protect the wearer from potential liquids or chemicals that might be present in the work environment. This barrier prevents liquids from permeating the suit and coming into contact with the skin.
Potential Risks of Insufficient Safety Gear
Not wearing proximity suits in the workplace of industries like metallurgy and foundry can expose workers to a range of serious risks and hazards. These suits are not just a piece of protective clothing; they are essential tools for ensuring worker safety in environments where extreme heat, molten metal, and other dangers are prevalent. Here are some of the risks associated with not wearing proximity suits:
1. Burns and Heat-Related Injuries
The primary purpose of proximity suits is to shield workers from intense heat and flames. Without these suits, workers are at a high risk of suffering burns and heat-related injuries due to direct exposure to extreme temperatures and molten metal splashes. Such injuries can range from minor burns to severe, life-threatening conditions.
2. Reduced Productivity and Efficiency
When workers are constantly concerned about their safety due to inadequate protective gear, their focus shifts from the task at hand to their well-being. This can result in reduced productivity and efficiency as workers are unable to perform their duties with full concentration and confidence.
3. Increased Downtime and Medical Costs
Injuries caused by not wearing proper protective gear can lead to extended periods of medical leave and downtime. This not only impacts the worker but also increases costs for the company due to medical expenses and lost productivity.

How Proximity Suits Protect Workers
Proximity suits are specifically designed to protect workers from a variety of hazards that are prevalent in extreme environments, particularly in industries like metallurgy and foundry. These suits act as a comprehensive defense mechanism, offering a barrier against several potential dangers. Here are some of the key hazards that proximity suits protect workers from:
1. Extreme Heat and Flames
Proximity suits are primarily designed to shield workers from extreme heat and flames. They prevent direct contact between the wearer's skin and intense heat sources, reducing the risk of burns and heat-related injuries that can occur in high-temperature work environments.
2. Molten Metal Splashes
Working with molten metals, such as iron, steel, or aluminum, carries the risk of splashes or spills that can cause severe burns upon contact with the skin. Proximity suits offer protection against these molten metal hazards, acting as a barrier to prevent skin exposure.
3. Clothing Ignition
In environments where flames or sparks are present, regular clothing can easily catch fire. Proximity suits are designed to resist ignition and prevent the spread of flames, minimizing the risk of clothing-related fires.
4. Radiant Heat
Radiant heat is a type of heat transfer that occurs without direct contact between the heat source and the object being heated. Proximity suits' insulating layers provide a barrier against radiant heat, protecting workers from prolonged exposure to high temperatures in foundries. A fire proximity suit is more specifically designed for handling high radiant loads produced by industrial fires.
5. Hot Surfaces
In environments where equipment, machinery, or surfaces become extremely hot, the risk of accidental contact is significant. Proximity suits offer an additional layer of protection, reducing the risk of burns when workers inadvertently come into contact with hot surfaces.
6. Chemical and Liquid Hazards
In certain situations, proximity suits can incorporate moisture barrier layers to protect workers from contact with hazardous chemicals, liquids, or molten materials that might be present in the work environment.
7. Respiratory Hazards
Some proximity suits include built-in masks or hoods to provide respiratory protection. These features prevent workers from inhaling harmful fumes, dust, and other airborne contaminants, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and related health problems.
8. Electric Arcs and Flash Hazards
In industries involving electrical work, proximity suits can provide protection against electric arcs and flash hazards, reducing the risk of burns and injuries resulting from electrical discharges.
Proximity suits are a blend of cutting-edge technology, ergonomic design, and advanced materials, all combined to create a garment that acts as a shield against the harsh realities of extreme environments. These suits enable workers in metallurgy and foundry industries to perform their tasks with confidence, knowing that their safety is a top priority.